Antimalware Service Executable is a legitimate and crucial part of the Windows Security suite, specifically designed to protect your PC from malware and other security threats. While its function is essential for safeguarding your computer, this process, known as MsMpEng.exe, can sometimes consume an excessive amount of system resources like CPU and RAM. This may cause your PC to slow down significantly, making it frustrating to use. If you’re noticing high CPU usage, you’re not alone—many users face this issue.
In this guide, we will walk you through a series of solutions to resolve the high resource usage caused by the Antimalware Service Executable process. Whether it’s tweaking settings, running a manual scan, or using third-party tools, there are various methods to improve your PC’s performance without compromising security.
Should You Disable Antimalware Service Executable?
It is important to understand that Antimalware Service Executable is an integral part of Windows Defender, protecting your system from malware. While disabling it may seem like a tempting option to fix performance issues, doing so is not recommended, as it exposes your computer to potential threats. Even if you manage to disable the process temporarily, Windows Defender will automatically restart it, ensuring your system remains protected.

If the process is consuming too much CPU or RAM, it is likely due to Defender running a scan or dealing with malware. In such cases, troubleshooting should be the next step, rather than disabling the service entirely. Below, we’ll provide several effective ways to fix the issue without turning off Windows Defender.

1. Run a Manual Scan and Get Malwarebytes
One of the first steps you can take to reduce the impact of high CPU usage caused by Antimalware Service Executable is to run a manual scan. By doing so, you ensure that any potential threats are identified and removed.
To run a manual scan:
- Open Windows Security using Windows Search.
- Go to Virus & threat protection.
- Click on Scan options under the Quick Scan section.
- Select Full scan and click on Scan now.

While Windows Defender is effective, some users opt for Malwarebytes, a trusted third-party antivirus tool, to supplement or replace Defender. Malwarebytes can:
- Detect and remove malware that Defender might have missed.
- Reduce the system load by managing resource consumption.
It’s important to note that using two antivirus programs simultaneously on your PC is not recommended, as they may interfere with each other. Malwarebytes will automatically disable Defender if you choose to use it, which can help reduce the CPU and RAM usage caused by the Antimalware Service Executable process.
2. Turn Off and On the Real-Time Protection
In some cases, turning off and then turning on the Real-time protection feature of Windows Defender can help resolve issues with high resource usage. This is a simple method that has worked for many users experiencing performance slowdowns.
To toggle Real-time protection:
- Go to Windows Security > Virus & threat protection > Manage settings.
- Toggle off the Real-time protection switch.
- Wait a few moments and toggle it back on.

If the problem persists after turning Real-time protection off and on, try the next steps.
3. Change Windows Defender’s Schedule
Windows Defender runs periodic scans in the background, and these scans may occur when you’re actively using your PC, causing the CPU and RAM to spike. Changing the schedule of these scans to a time when you’re not using the computer can reduce the performance impact.
To adjust the schedule:
- Open Task Scheduler from Windows Search.

- Navigate to Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender.

- Right-click on the Windows Defender Scheduled Scan and select Properties.

- Uncheck Run with highest privileges and make other necessary adjustments.
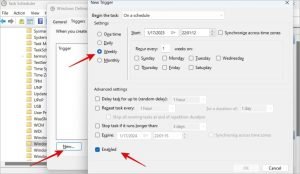
- Set a new schedule for the scan, such as weekly instead of daily.
4. Disable AntiSpyware via the Registry Editor
For certain users, an issue within the Registry Editor might be causing excessive CPU usage. Disabling the AntiSpyware feature can help resolve the problem. Here’s how you can fix it:
- Open Registry Editor with administrative privileges using Windows Search.
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender.
- Right-click on the empty area in the right pane and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name the file DisableAntiSpyware and set its value to 1.
- Save the changes and restart your PC.


5. Disable Exploit Protection Service
Sometimes, Windows Defender’s Exploit Protection service may fail to close certain processes, resulting in a loop that keeps Antimalware Service Executable running in the background, consuming excessive resources. You can stop this by disabling the Exploit Protection service.
To do this:
- Open PowerShell with administrative rights.
- Paste the following command and press Enter:
This command will disable the Exploit Protection service, reducing the load on your system.
6. Clean Boot and Reset Option
Performing a clean boot can help identify any third-party programs or services that may be contributing to the high resource usage. A clean boot starts Windows with the minimum required drivers and programs.
To perform a clean boot, follow Microsoft’s guide on how to troubleshoot problems with a clean boot. Once done, you can reset your PC to return to normal mode.
7. Add MsMpEng.exe to Exclusion List
Antimalware Service Executable scans itself during the process, which may create a loop that results in high CPU and RAM usage. You can prevent this by adding MsMpEng.exe to the exclusion list.
Here’s how:
- Open Microsoft Defender.
- Go to Virus & threat protection > Manage settings.
- Scroll down to Exclusions and click on Add or remove exclusions.
- Click Add an exclusion, select Process, and type MsMpEng.exe.


By excluding the process from being scanned, you can reduce the CPU load.
Conclusion
The Antimalware Service Executable process is crucial for maintaining your system’s security, but it can sometimes lead to performance issues due to excessive CPU and RAM usage. Rather than disabling it, follow the methods outlined above to troubleshoot and resolve the issue. From running manual scans to adjusting system settings, these steps can help optimize the process without compromising your PC’s security.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I disable Antimalware Service Executable completely?
No, it is not recommended to disable it, as it’s essential for protecting your PC from malware. Disabling it leaves your system vulnerable.
2. Does installing another antivirus stop Antimalware Service Executable from running?
No, even if you install another antivirus like Malwarebytes, Windows Defender will continue running in the background, which includes Antimalware Service Executable.
3. Why is Antimalware Service Executable using so much CPU?
High CPU usage typically occurs when Windows Defender is running a scan. If the process is using excessive resources constantly, troubleshooting steps like adjusting the scan schedule or turning off real-time protection may help.
4. How can I stop Antimalware Service Executable from scanning itself?
You can add MsMpEng.exe to the exclusion list in Microsoft Defender settings to prevent it from scanning itself, which can help reduce resource usage.
5. Is Malwarebytes a good alternative to Windows Defender?
Malwarebytes is a trusted antivirus program that can complement or replace Windows Defender, but using two antivirus programs simultaneously is not recommended due to potential conflicts.
